What is sciatica?
Sciatica (also known lumbar radiculopathy) is a type of pain affecting one or more sciatic nerve roots, which extend from your lower back (lumbar spine) down into the back of each leg.
What causes sciatica?
Sciatica (also known lumbar radiculopathy) is a type of pain affecting one or more sciatic nerve roots, which extend from your lower back (lumbar spine) down into the back of each leg.
What causes sciatica?
What are the symptoms of sciatica?
Common symptoms
of sciatica:
- Lower Back pain, which may be a
mild ache, or a debilitating-sharp, burning sensation
- Weakness, pain, numbness
and/or tingling in the lower extremities
- Discomfort when
sneezing, coughing or laughing
- Pain that may
worsen at night, interrupting your sleep
- Heel walk, which is the decreased ability to bring your foot upward
- Drop foot (difficulty when
flexing your ankle and bring up the front of your foot)
- Restricted ability to walk on your
tiptoes, walk, drive and/or lift your heel off the ground
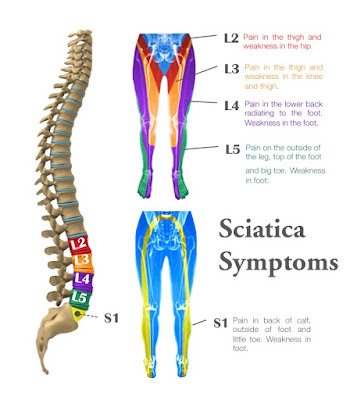 |
| Figure 2: Mapped symptoms of sciatica by vertebrae number and extremity locations. |
 |
| Watch this online video about sciatica. |
How is sciatica diagnosed?
Procedures used to diagnose sciatica may include:
- A straight-leg
raise test to induce pain radiating from the hip and down the
leg.
- A foot-flex or Braggard’s Test
to identify sciatic nerve symptoms
- Magnetic
resonance imaging (MRI) is used to get detailed images of
spinal discs. MRIs use a giant magnet that circles the body.
- Computerized
tomography (CT) scan with myelogram is an X-ray used with
a special dye injected into the spinal fluid. The CT scan is used to help
identify the “bony” causes of spinal stenosis, while the dye helps
diagnose soft tissue conditions such as disc herniation or a bulge.
- Selective
nerve root block (SNRB) is when a local anesthetic is
injected into a nerve root suspected of being affected by spinal stenosis.
If the patient’s pain goes away after the injection, it can be determined
that the compressed nerve is the cause of pain.
How is sciatica treated?
Typically, a combination of treatments works best to treat spinal stenosis. Treatment options may include:
Typically, a combination of treatments works best to treat spinal stenosis. Treatment options may include:
- Education—teaching patients spinal anatomy and basic body mechanics to help them manage their condition
- Exercise
- Activity modification
- Medication
- Physical therapy
- Injections
- Surgery
Does sciatica require surgery?
In some cases, surgery is required. SpineOne is dedicated to minimally invasive options whenever possible and will do everything we can to avoid surgery.
In some cases, surgery is required. SpineOne is dedicated to minimally invasive options whenever possible and will do everything we can to avoid surgery.
When can I expect to
resume normal activities without sciatica?
Many people with sciatica are able to resume their normal
activities after treatment. The goal of treatment for most patients is to
have a healthy, active lifestyle free of sciatic pain. You’ll want to
speak with a physician who
specializes in spinal care to plan your particular treatment and get
back in the swing of things.
Where can I get treatment for sciatica?
If you suffer from chronic or acute back pain and cannot find relief, you should always contact a spine specialist like the physicians at SpineOne. SpineOne offers a comprehensive evaluation, diagnosis and treatment plan tailored to meet the needs of each individual patient. The physicians at SpineOne perform minimally invasive procedures combined with other practices to get you back on your feet and enjoying your life again.
SpineOne provides doctor consultations, MRIs and treatments
all from the same facility for your convenience. Same-day
appointments are also available upon request.
Visit www.SpineOne.com or
call 303.500.8611 today.


